Anxiety is a natural and common emotion characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, and apprehension. It is a normal response to stressful or potentially dangerous situations, and it can be beneficial in moderation as it helps us stay alert and prepare for challenges. However, when anxiety becomes excessive, persistent, and disproportionate to the situation, it can develop into an anxiety disorder that interferes with daily life and well-being.
While occasional anxiety is a part of life, individuals with anxiety disorders experience frequent, intense, and excessive anxiety and fear that can significantly impair their ability to function normally. Anxiety disorders can manifest in various forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, agoraphobia, separation anxiety disorder, and others.
It is important to note that anxiety affects people differently, and the severity, duration, and specific symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience primarily physical symptoms, such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, or muscle tension, while others may experience more psychological symptoms, such as excessive worry, intrusive thoughts, or a sense of impending doom.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders is crucial for recognizing their distinct symptoms and navigating the appropriate treatment options.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, family, or finances. People with GAD experience chronic and exaggerated anxiety and tension, even when there is little or no apparent reason for concern.
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Social Anxiety Disorder, also known as social phobia, is an intense fear of social situations where an individual may be scrutinized, judged, or embarrassed by others. People with SAD experience overwhelming anxiety and self-consciousness in social interactions, leading to avoidance of social situations or intense distress when they cannot be avoided.
Panic Disorders or Panic Attacks
Panic Disorder is characterized by recurrent and unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear or discomfort accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, and a feeling of impending doom.
People with Panic Disorder live in constant fear of experiencing another panic attack, which can lead to avoidance of situations or activities that they associate with panic attacks.
Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear of situations or places where it might be difficult to escape or receive help in case of a panic attack or other embarrassing situation. People with agoraphobia may avoid public transportation, crowded places, or even leaving their homes due to fear of experiencing anxiety or panic symptoms.
Separation Anxiety
Separation Anxiety Disorder is characterized by excessive anxiety or fear about being separated from a person or place that provides a sense of security or attachment. While separation anxiety is common and developmentally appropriate in young children, it can become a disorder when the anxiety becomes excessive, persistent, and inappropriate for the individual’s age or developmental stage.
Mixed Anxiety and Depressive Disorder
Mixed Anxiety and Depressive Disorder, also known as Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia) with Anxious Distress, is a condition characterized by symptoms of both anxiety and depression. Individuals with this disorder experience persistent low mood, lack of interest or pleasure in activities, and symptoms of anxiety such as excessive worry, restlessness, and irritability.
Postpartum Anxiety
Postpartum Anxiety is a type of anxiety disorder that can develop in women after giving birth. It is characterized by excessive worry, intrusive thoughts, and physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat, trembling, and difficulty sleeping.
Unspecified Anxiety Disorder
Unspecified Anxiety Disorder is a category used when an individual’s symptoms of anxiety do not meet the specific criteria for any of the other anxiety disorders but cause significant distress or impairment in daily functioning.
Symptoms of Anxiety

Anxiety disorders can manifest with a wide range of physical and psychological symptoms. Some common symptoms of anxiety include:
- Excessive worry or fear
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Sleep disturbances (difficulty falling or staying asleep)
- Fatigue
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Shortness of breath
- Stomach or digestive problems
It is important to note that everyone experiences anxiety differently, and the specific symptoms and their intensity can vary from person to person.
Symptoms in Men vs. Women
While anxiety disorders can affect both men and women, there are some differences in how symptoms may manifest or be experienced based on gender.
In general, women are more likely to experience anxiety disorders than men, and they may be more likely to report symptoms such as excessive worry, feelings of panic, and physical symptoms like muscle tension or fatigue.
Men, on the other hand, may be more likely to experience symptoms such as irritability, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. They may also be more likely to engage in avoidance behaviors or self-medication (such as alcohol or substance use) to cope with their anxiety.
However, it is important to note that these are general trends, and individuals of any gender can experience a wide range of anxiety symptoms.
Severe Anxiety Symptoms
In some cases, anxiety symptoms can become severe and disruptive to daily life. Severe anxiety symptoms may include:
- Frequent and intense panic attacks
- Persistent and overwhelming worry or fear
- Avoidance of situations or activities due to anxiety
- Difficulty functioning at work, school, or in social situations
- Physical symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, or nausea
- Intrusive and distressing thoughts or images
If anxiety symptoms are severe and interfere significantly with daily functioning, it is important to seek professional help from a mental health professional. Severe anxiety can be a sign of an underlying anxiety disorder that requires proper treatment and management.
Anxiety in Specific Contexts

Social Anxiety
Social anxiety is a persistent fear or anxiety about social situations, often stemming from a fear of being judged, embarrassed, or rejected by others. Strategies to manage social anxiety may include:
- Gradually exposing oneself to social situations
- Challenging negative thoughts and beliefs about social situations
- Developing social skills and assertiveness
- Joining a support group or seeking counseling
- Using relaxation techniques before and during social interactions
Performance Anxiety
Performance anxiety is a type of anxiety that can arise in situations where an individual is expected to perform or deliver, such as public speaking, playing a musical instrument, or taking an exam. Coping strategies for performance anxiety may include:
- Practicing and preparing thoroughly
- Using relaxation techniques before and during the performance
- Challenging negative self-talk and perfectionism
- Visualizing successful outcomes
- Seeking support from a coach or mentor
Treatment and Management
The treatment approach for anxiety disorders typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication, depending on the severity and specific type of anxiety disorder.

Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective forms of psychotherapy for anxiety disorders. CBT aims to help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. It teaches coping strategies, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and gradual exposure to feared situations or triggers.
Other forms of therapy that may be helpful for anxiety include:
- Exposure therapy
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT)
- Interpersonal therapy
- Psychodynamic therapy
Karmic Cord Cutting Therapy
Karmic Cord Cutting is an emotional release therapy designed to address and resolve deep-seated emotional blockages stemming from various life circumstances. These emotional blockages are potent, often invisible barriers that can profoundly affect an individual’s life. They act like unseen chains, hindering one’s ability to reach their full potential, impacting personality, relationships, and overall well-being. At their core, emotional blocks result from unresolved feelings and experiences that have solidified into deep-seated patterns. The consequences of emotional blockages are significant and far-reaching, impacting various aspects of life:
- Personal Growth and Self-Expression: Emotional blocks can severely limit an individual’s capacity for personal development and self-expression.
- Relationships: These blocks impair the ability to form and maintain healthy relationships, affecting both personal and professional interactions.
- Authentic Living: They often create a disconnect, preventing individuals from living a truly authentic and fulfilling life.
Specific Treatments for Panic and Social Anxiety Disorders
For panic disorder, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often combined with exposure therapy, which gradually exposes individuals to situations that trigger panic attacks in a controlled and safe environment. Medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines, may also be prescribed to manage panic symptoms.
In the case of social anxiety disorder, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is typically used to challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs about social situations. Exposure therapy, which involves gradually exposing individuals to feared social situations, is also commonly used.
Combining Treatments for Depression and Anxiety
Many individuals with anxiety disorders also experience symptoms of depression, or vice versa. In such cases, an integrated treatment approach that addresses both conditions may be necessary. This can involve a combination of psychotherapy (such as CBT or interpersonal therapy) and medication (such as antidepressants) to manage the overlapping symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Self-Help and Coping Strategies
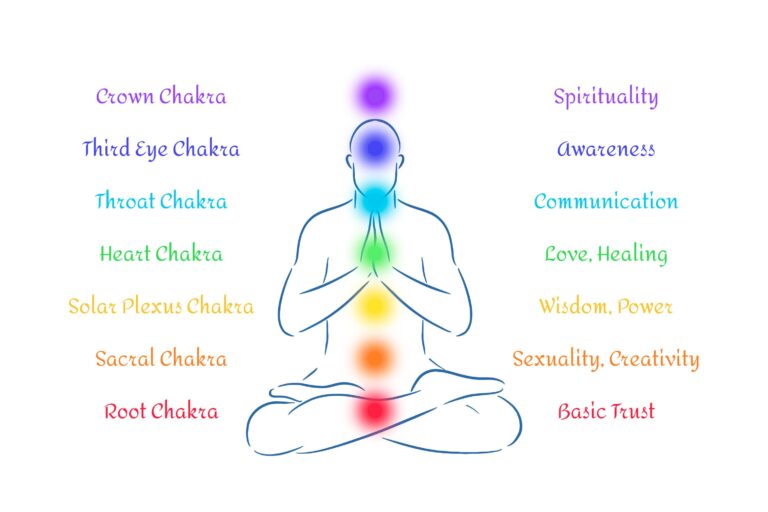
Chakra Healing Meditation
This form of meditation focuses on the seven key energy centers, or chakras, distributed along the spine. These chakras are vital for maintaining physical, emotional, and spiritual harmony. By engaging in chakra healing meditation, you can:
- Unblock Energy Centers: Emotional or physical stress can lead to blockages in the chakras, manifesting as various symptoms. Chakra meditation aims to identify and release these blockages, promoting a free flow of energy.
- Reduce Anxiety: Regularly balancing the chakras helps to decrease anxiety by stabilizing the emotional responses triggered by the energy centers. This can lead to a calmer mind and a more balanced emotional state.
- Enhance Well-being: When the chakras are aligned and open, it enhances overall wellness, helping you to feel more grounded and connected to yourself and the world around you.
Specific Chakras Focus:
Root Chakra (Muladhara): Balancing the root chakra, located at the base of the spine, helps in establishing a foundation of stability, security, and a sense of grounding. This is crucial for managing fears and anxiety related to basic survival and safety.
Solar Plexus Chakra (Manipura): This chakra, situated in the abdomen, is the center of personal power and self-confidence. Balancing the solar plexus chakra can significantly reduce feelings of helplessness and stress, and enhance one’s ability to make decisions and assert personal control.
Regular meditation on these chakras, particularly through guided practices offered by experts like Dr. Saraah Chimthanawala, can lead to profound changes in how energy flows through your body, directly influencing your emotional health and resilience.
Natural Anxiety Relief
Some individuals may find relief from anxiety symptoms through the use of natural remedies or supplements, such as:
- Herbal supplements (e.g., chamomile, lavender, valerian root)
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Vitamin B complex
- Magnesium
- L-theanine
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any natural remedies or supplements, as they can interact with medications or have side effects.
Practical Tips for Managing Anxiety
In addition to professional treatment, there are various self-help strategies that can be effective in managing anxiety:
- Practice relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation)
- Engage in regular physical exercise
- Maintain a balanced diet and good sleep hygiene
- Practice mindfulness and meditation
- Limit caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine intake
- Engage in leisure activities and hobbies
- Build a strong support system
Support and Community

Finding Support Groups
Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can provide a sense of community, validation, and support. Support groups for anxiety disorders can be found through mental health organizations, local hospitals or clinics, or online forums and communities.
Resources and Help
There are various resources available for individuals seeking information, support, or professional help for anxiety disorders:
- National mental health organizations and helplines
- Online directories for finding therapists or counselors
- Mental health clinics and treatment centers
- Educational resources and self-help materials
Conclusion and Encouragement
Anxiety is a common and natural emotion, but when it becomes excessive, persistent, and disproportionate to the situation, it can develop into an anxiety disorder that significantly impacts daily life. This comprehensive guide has covered various types of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, and effective treatment options, including psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies.
Encouragement to Seek Professional Help If you or a loved one is struggling with anxiety, it is important to seek professional help from a mental health professional. Anxiety disorders are treatable, and with the right support and resources, it is possible to manage symptoms and regain control over your life. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and taking proactive steps towards better mental health can lead to a more fulfilling and less anxious life.